How Does Red Light Therapy Work?

Red Light Therapy 101: Learn the Basics of Red & Near Infrared (NIR) Light

Red vs Near Infrared Light
- Red light: Visible to the human eye, red light has wavelengths between 600–700 nanometers (nm) and is most effective on the skin's surface. Red light can improve skin health, collagen production, as well as help with hair growth.
- Near-infrared Light: Invisible to the human eye, near-infrared light has wavelengths between 700–1200 nm and can penetrate deeper into the body, acting on the muscles, joints and bone.
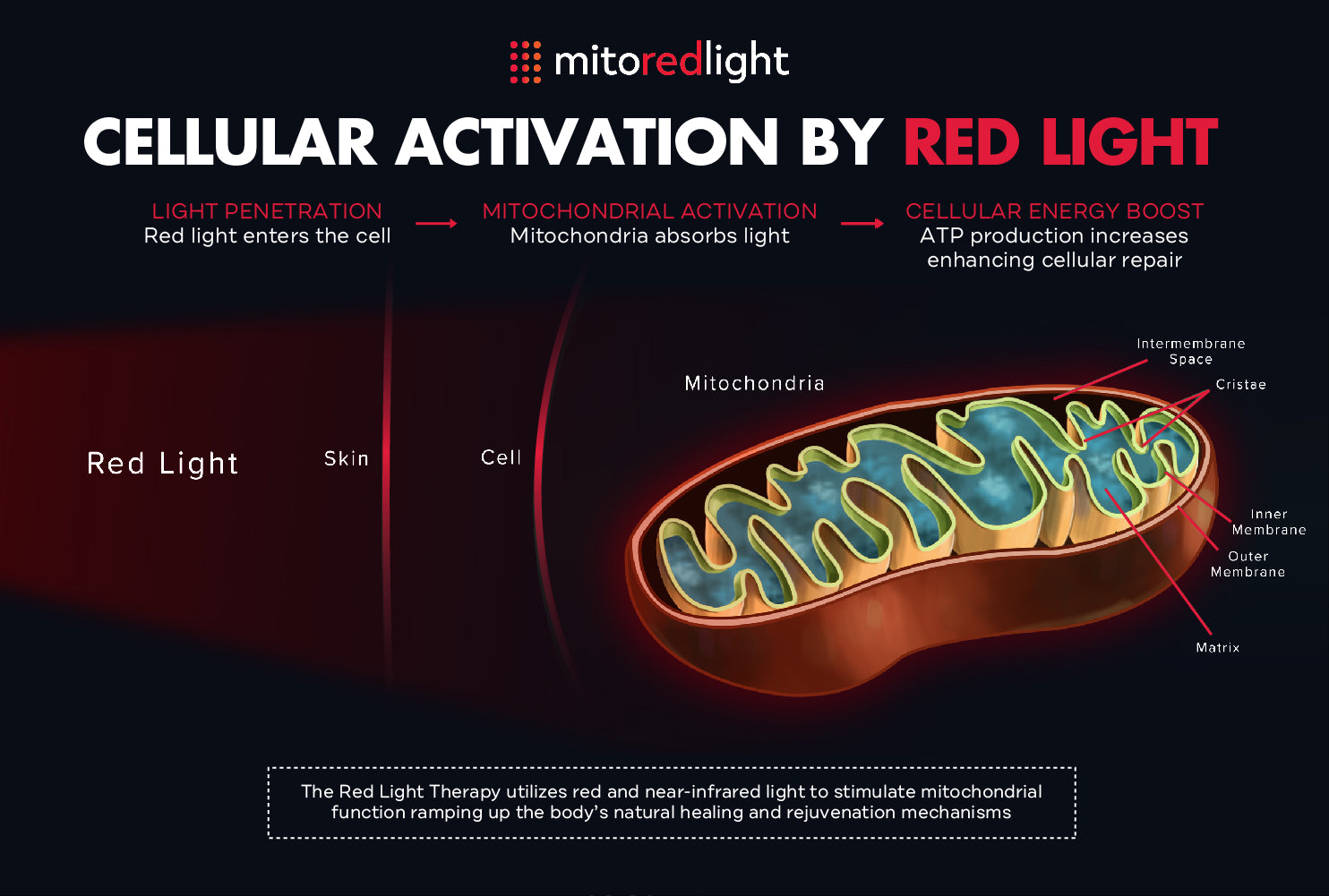
The Science Behind RLT
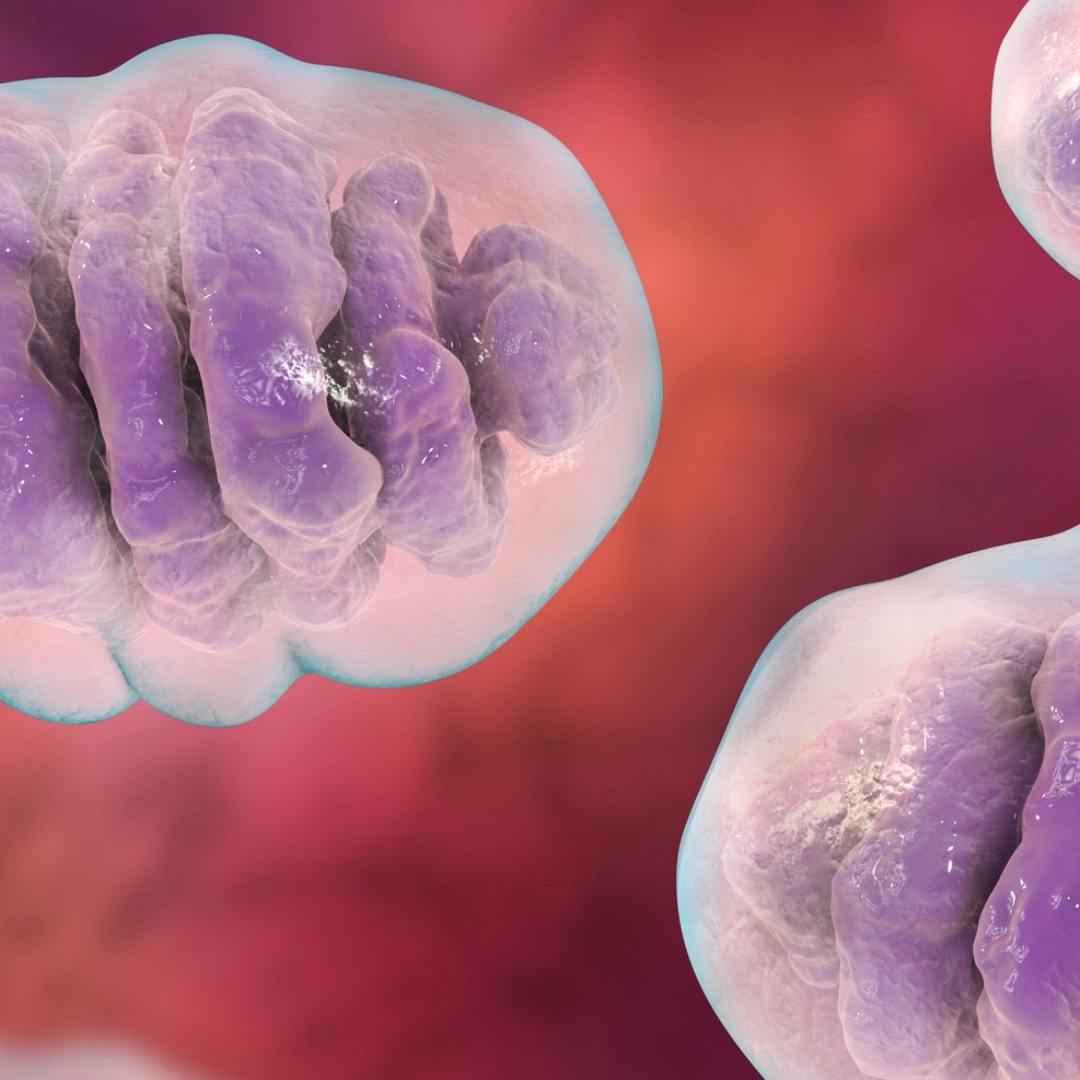
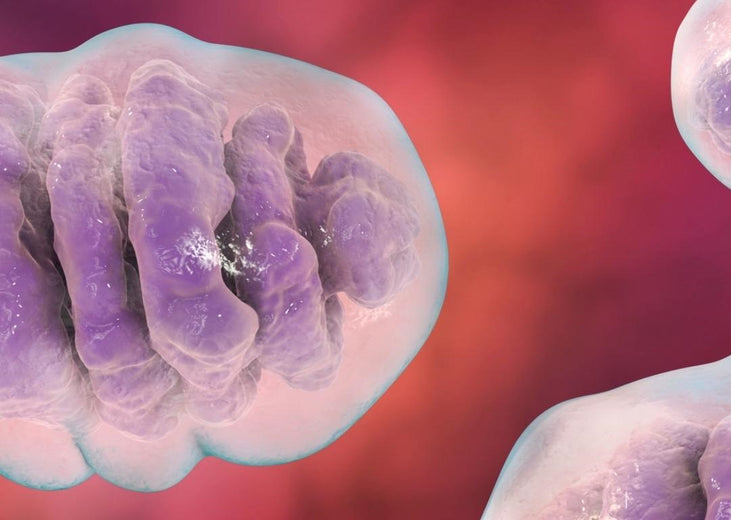
The best-studied mechanism of action surrounding red and near-infrared light therapy is the stimulation of mitochondrial energy production in the cells. Mitochondria are tiny organelles (organs within a cell) that produce all of the energy that our cells and our bodies ultimately need.
All molecules and atoms absorb very specific wavelengths of light. The specific molecule within the mitochondria that is thought to absorb red and near-infrared light is a chemical called cytochrome C oxidase. Cytochrome C oxidase plays an absolutely essential role in transferring electrons down an electrochemical gradient in mitochondria called the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain is what drives the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is a complex organic molecule that is considered the “currency” of energy in the body.
Red light therapy is ultimately thought to improve the efficiency and speed of the electron transport chain, improving the availability of ATP in the cells and throughout the body. This increased energy is what is thought to provide the many benefits that red light therapy is used for.
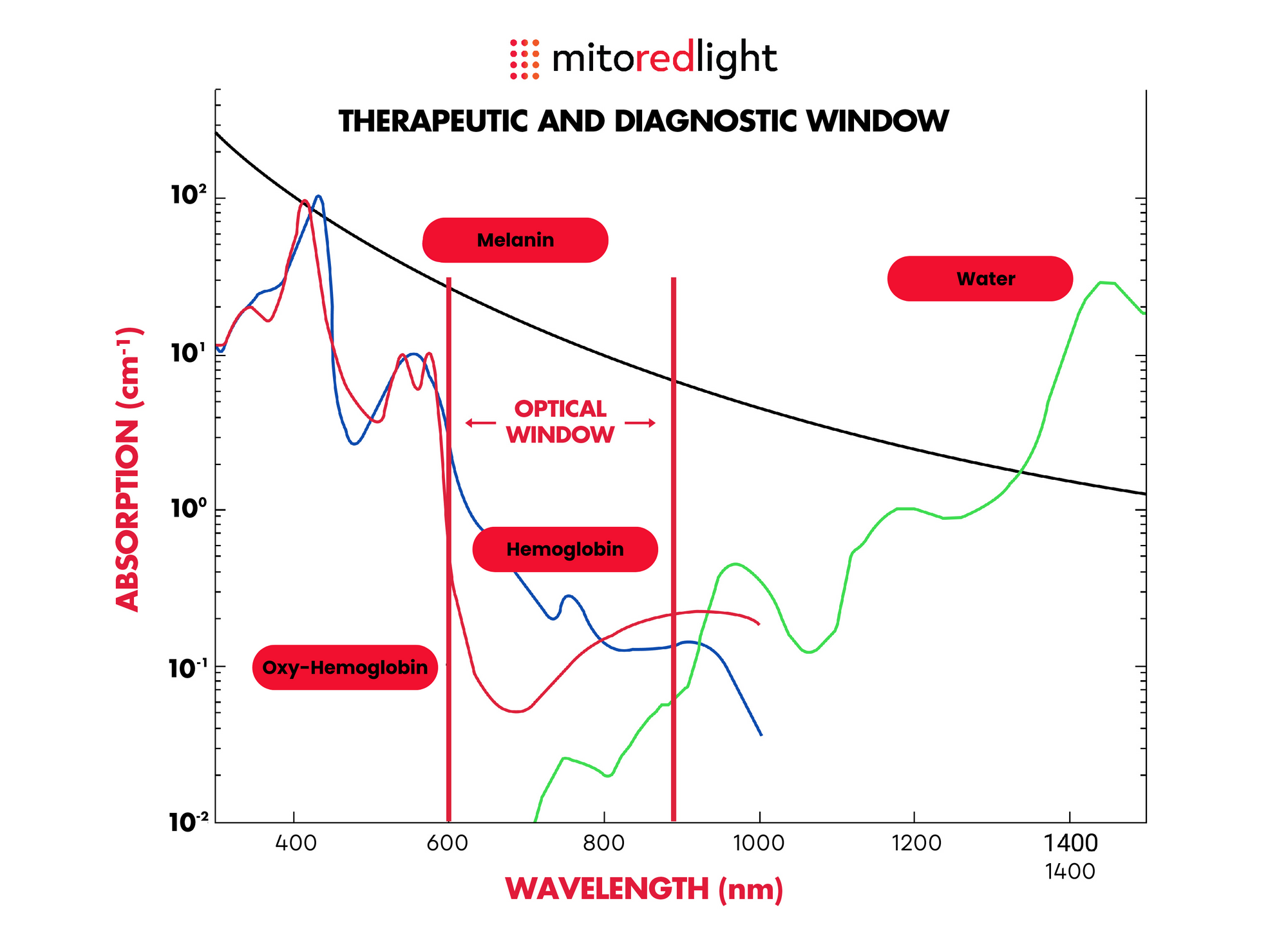
The Optical Window
The Optical Window or therapeutic window, defines the range of wavelengths where light has its maximum depth of penetration in tissue.
The window is primarily limited by the light absorption of blood at short wavelengths (below 600nm) and water at long wavelengths (above 900nm).
Mito Red Light devices specifically use wavelengths in the 'optimal' part of the optical window to ensure maximum tissue penetration and mitochondrial activation.
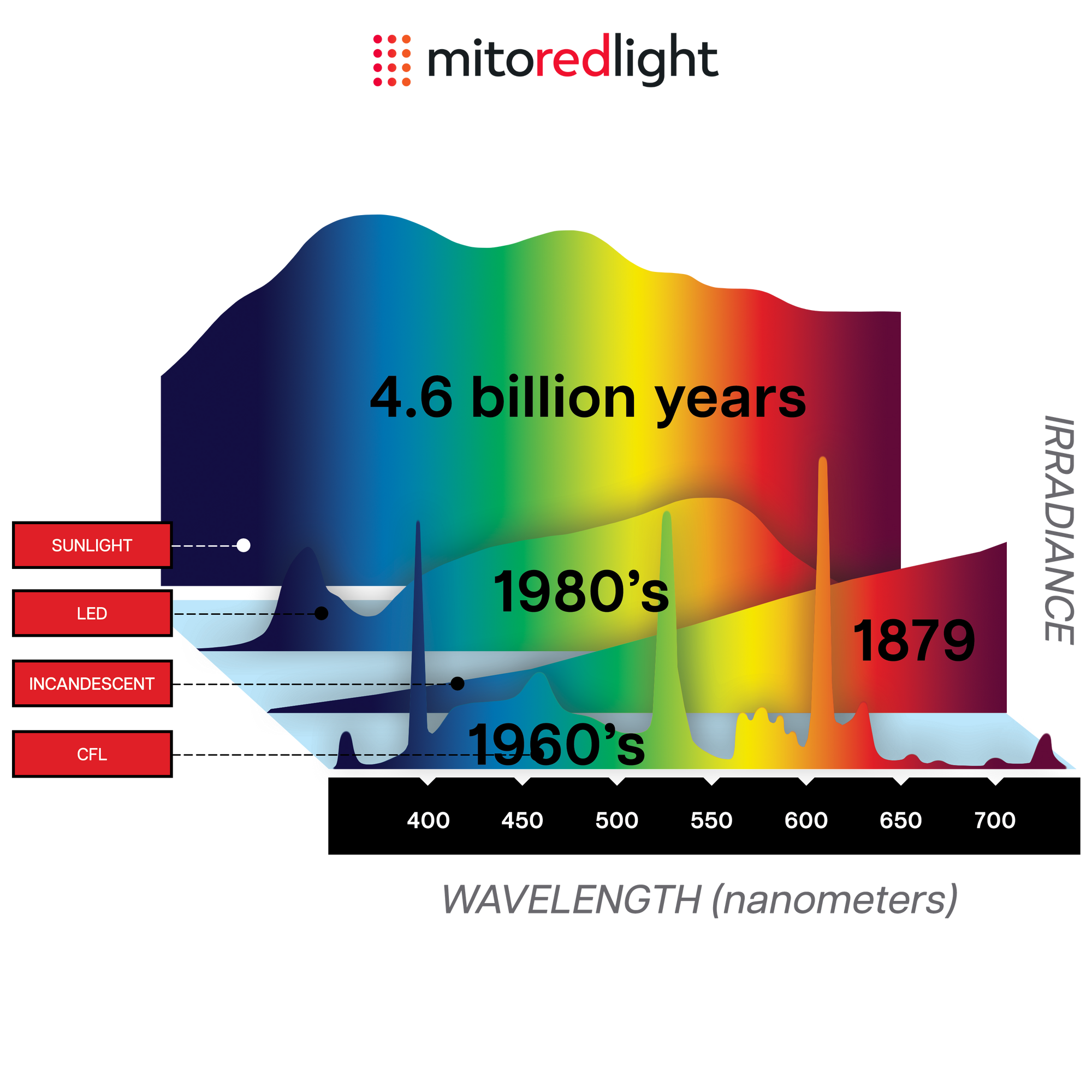
Modern Humans are "Mal-Illuminated"
The human body requires light to function, with light having an important role in many biological processes The solar spectrum is made up of UV, Visible and Infrared light with each part of the spectrum having important and distinct biological effects., For example UVB light is needed to make vitamin D and blue light helps regulate our body’s circadian rhythm.
While light plays many important roles in health, modern humans are spending less and less time exposed to sunlight. Our housing, transport, and workspaces are often indoors, reducing our exposure to the beneficial health effects of natural sunlight.
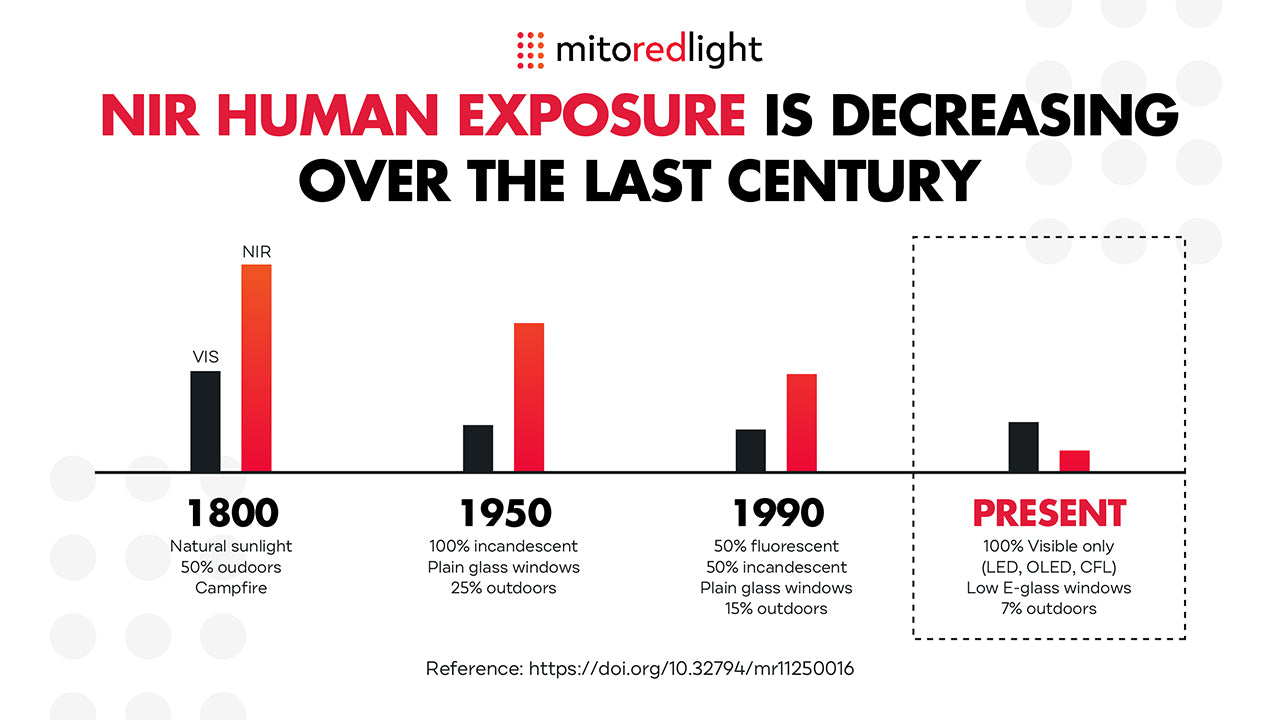
Modern Humans are Red and Near Infrared Light Deficient
As shown above, modern LED and CFL lighting is lacking in the beneficial wavelengths of red and near infrared light. In addition the irradiance (intensity) of indoor lighting is significantly lower than that of natural sunlight (even on a cloudy day!)
Furthermore, energy-efficient windows in buildings and vehicles further limit our exposure to these wavelengths of light.
Taken together, our indoor lifestyles and modern indoor lighting, humans have experienced a massive decrease in their exposure to these beneficial wavelengths of light over just the last 100 years.
Viewed from this perspective, 'supplementing' with red and near infrared light using a high quality, well designed and constructed LED light therapy device, makes a lot of sense!

More ATP = Improved Cellular Function
Because red and near infrared light act on the mitochondria increasing ATP, there are a myriad of potential benefits.
If a cell contains mitochondria (which all cells in the human body do except red blood cells) there is the potential for them to benefit from red and near infrared light.
The bottom line is that when your cells have more energy at their disposal, they simply function better!
Backed by Science and Research

Supports Health Inflammatory Response
Everything You Need to Know About Red Light Therapy and INFLAMMATION


Supports Muscle Recovery
Everything You Need to Know About Red Light Therapy and MUSCLE RECOVERY

Supports Hair Growth
EVERYTHING you need to know about Red Light Therapy and Hair Growth.
Supports Cognitive Health
Everything You Need to Know About Red Light Therapy and BRAIN HEALTH

Supports Weight Loss Routine
Everything You Need to Know About Red Light Therapy and WEIGHT LOSS