Medically reviewed by Dr. Benjamin Vincent
Key Takeaways:
- Red light therapy cannot produce vitamin D or treat vitamin D deficiency.
- Only ultraviolet (UVB) light can trigger the skin to synthesise vitamin D.¹
- Red light therapy still offers meaningful wellness benefits that complement, but do not replace, vitamin D-focused strategies.
Vitamin D synthesis in the skin requires ultraviolet B (UVB) light, which is not emitted by red or near-infrared LEDs.¹
However, that doesn’t make red light therapy (RLT) any less valuable. It just means RLT plays a different role. Photobiomodulation (PBM) supports cellular energy, skin health, recovery and inflammation in ways that are completely separate from the UVB-driven pathway your body uses to make vitamin D.²˒³
At Mito Red Light, we want users to be crystal clear on that distinction. In this guide, we’ll break down how vitamin D is actually made, what RLT does, and what you can do to correct a vitamin D deficiency.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D plays a role in far more than most people realise. It’s a fat-soluble nutrient that your body depends on for foundational functions—especially bone strength, immune health and calcium absorption.
Where things get complicated is how common low levels of vitamin D have become. Modern indoor living, limited sunlight, certain health conditions and even geography all contribute to its widespread deficiency.
Current estimates show that more than 50% of the global population is vitamin D-deficient or has suboptimal levels at any given time.⁴˒⁵ And because vitamin D influences so many systems, low levels don’t stay quiet for long.
What Are the Signs of Low Vitamin D?
Vitamin D deficiency can affect the body in multiple ways, including:
- Reduced calcium absorption, leading to weaker bones
- Increased risk of fractures or conditions like rickets and osteomalacia
- Impaired immune function
- Higher susceptibility to chronic health issues
- Muscle weakness or low energy
- Mood changes linked to insufficient vitamin D
Some groups of people are more prone vitamin D to deficiency. These include:
- Older adults
- Individuals with minimal sun exposure
- People with darker skin tones
- Anyone living in northern climates
- Those with malabsorption conditions
- Individuals who wear full-coverage clothing daily
How Does the Body Produce Vitamin D?
Your body has a built-in system for making vitamin D, but it only switches on under one particular condition: exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) light.¹ This is the key distinction most people miss. Visible light, red light and near-infrared light don’t activate this pathway only UVB does.
When UVB rays hit the skin, they interact with a compound called 7-dehydrocholesterol, converting it into vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). From there, the liver and kidneys turn that raw material into the active, usable form of vitamin D.⁶
This is the only way your body makes vitamin D on its own, which is why spending time in the right kind of sunlight still matters, and why light type (not brightness) is the whole story.
What Is Red Light Therapy?
Red light therapy (RLT) is often confused with sunlight because both involve light exposure, but they behave completely differently in the body. RLT doesn’t use UV light at all. Instead it works in the visible red and near-infrared ranges, which support cellular function in ways unrelated to vitamin D.
Because these wavelengths don’t contain UV radiation, they cannot trigger vitamin D production. Instead, RLT is known for supporting:
- Skin rejuvenation and collagen activity
- Inflammation management
- Muscle recovery
- Sleep quality and circadian rhythm support
- Cellular energy production (ATP)
The benefits are real, just completely different from what UVB light does.²
How Are Red Light Therapy and UVB Light Different for Vitamin D?
Now that both pathways are clear, the distinction becomes straightforward. RLT and UVB light sit in completely different parts of the spectrum and trigger entirely different biological responses.
Red light therapy uses visible red and near-infrared wavelengths (about 620–1100 nm) that support cellular repair, energy production and reduced inflammation. Conversely, UVB light occupies the much shorter 280–320 nm range the only band of light capable of activating the chemical reaction in the skin that produces vitamin D.
Because they act on different structures, their uses diverge. For instance RLT is commonly used for skin rejuvenation, recovery, mood and sleep support, while UVB is used to treat vitamin D deficiency and certain dermatological conditions.
Furthermore, these two have different effects on the skin. Whereas: red light doesn’t tan or burn the skin, UVB can cause tanning or sunburn with overexposure. This is why RLT is generally safe for all skin types while UVB requires careful, controlled use.
Scientific Evidence on Red Light Therapy and Vitamin D Production
RLT does not increase vitamin D levels. Multiple studies have tested this, and the results are consistent. There is no evidence that RLT increases vitamin D levels.⁷ This is because the wavelengths used in RLT simply don’t have the right amount of energy to trigger vitamin D synthesis.
A lot of confusion online comes from mixing up different forms of light therapy. So here’s how the myths stack up against what the science actually shows.
What Are the Benefits of Red Light Therapy?
Although RLT doesn’t create vitamin D, it still plays a supportive role in overall skin health — and healthier skin can influence how well your body handles UV exposure.²
Research shows that RLT benefits the skin and reduces inflammation. By supporting the resilience of the skin, RLT may help people tolerate safe sun exposure.
UVB rays need to reach specific layers of the skin for efficient vitamin D synthesis. When the skin is inflamed, easily irritated or overly thin which can happen with age UVB exposure can feel harsher or become harder to tolerate. Some studies suggest that RLT may support epidermal thickness and collagen networks, potentially making the skin healthier and less prone to damage.
For older adults, people with sensitive skin or anyone who burns easily, combining good sun habits with a regular red light routine may create a better overall environment for vitamin D synthesis not because RLT makes vitamin D, but because it can help the skin stay strong, calm and functional.
How To Address Vitamin D Deficiency
If your vitamin D levels are low, the good news is that the most effective fixes are simple and well-studied.
For most people, natural sunlight is the best source of vitamin D, because UVB rays are essential for vitamin D synthesis. Spending short, safe periods outdoors is often enough to help maintain healthy levels. Just be mindful of your skin type, location and season since sunlight strength varies more than most people realise.
Food can help too.⁸ Focus on foods like:
- Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel
- Egg yolks
- Beef liver
- Fortified milks or cereals
Supplements are often recommended when sunlight or diet alone isn’t enough. They’re especially helpful for people who live in northern climates, work indoors, have darker skin or have challenges with absorption. Your healthcare provider can tell you whether you need vitamin D2, D3 or a specific dose.
During winter or in situations where sunlight is limited, UVB lamps can be an option but this is where caution matters. Because they deliver actual ultraviolet light, UBV lamps come with sunburn risk and need to be used under clear guidelines (and ideally under medical supervision).
If you’re unsure where you stand, a simple blood test that measures serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D can show whether you’re low, borderline, or already in a healthy range. This test is quick, inexpensive and a much better strategy than guessing.
Safety Considerations When Using Light Therapy for Vitamin D
Light therapy can be incredibly useful, but only when you understand the safety differences between red light and UVB light. These two are not interchangeable, and they do not carry the same risks.
Red light therapy is generally safe for all skin types and does not burn or tan the skin because it doesn’t use UV light. That’s why people can use RLT daily without worrying about sun damage. Conversely, UVB light needs a much more careful approach. Because it contains the same wavelengths that cause sunburn, UVB exposure comes with real risks like skin irritation, burning, and increased long-term skin cancer risk. This doesn’t make UVB therapy “bad” it just means that UVB therapy must be used intentionally and never casually.
Anyone considering UVB lamps for vitamin D should get guidance from a healthcare professional, especially if:
- You burn easily
- You have a history of skin cancer
- You’re photosensitive
- You’re already supplementing, but still have low levels
If you have vitamin D deficiency and are not improving despite sunlight, supplements, or lamps that’s another sign to loop in your provider.
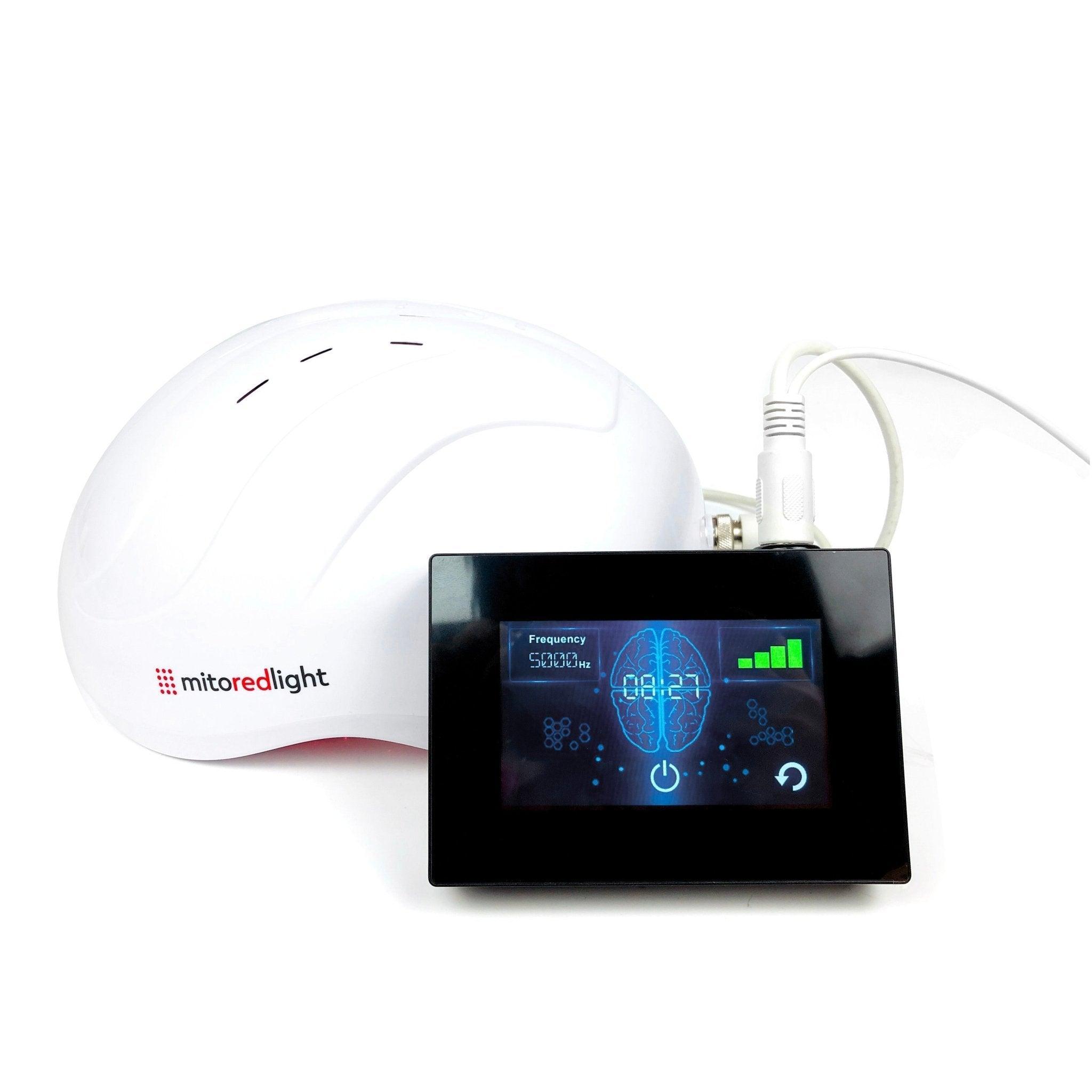
MitoSOLIS: UVB Light Therapy
We built MitoSOLIS to make narrowband UVB simple, precise and easy to fit into real life. Our UVB lamp uses patented LED engineering tuned primarily to the 305–313 nm UVB range, with stringent component screening. Narrowband UVB in the 305–313 nm range interacts with natural 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin, which can kick off the body’s own process for making vitamin D.
Sessions are brief (about two to four minutes per use), and our system is app-controlled so you can personalise time and track usage over weeks. Unlike legacy fluorescent “vitamin D” lamps that can have broader, less targeted spectra, MitoSOLIS focuses on narrowband UVB and is third-party tested for spectrum.
MitoSOLIS gives you a controlled, narrowband UVB option to help support your body’s own vitamin D pathway, with tools to track time, stay consistent, and keep safety front and centre.
The Bottom Line
RLT can not correct vitamin D deficiency. Instead, focus on supplements, spending time outdoors and balanced diet. RLT can complement your wellness routine, working to support overall skin health and integrity.
If you’re looking for effective ways to manage vitamin D levels, MitoSOLIS was designed to make it easier to support vitamin D production when sunlight is limited or schedules are tight.
DISCLAIMER : Mito Red Light devices are Class II wellness devices aimed at affecting the body through supporting cellular function. The information provided in this article and on this site is for educational purposes only, and is not intended to imply the effectiveness of Mito Red Light devices for any specific application. The information provided in this article and on this site is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. It is not a substitute for consultation with a licensed medical provider and should not be construed as medical advice. Click here to read our article on potential contraindications of red light therapy.
FAQs
Can red light therapy treat vitamin D deficiency?
No. Red light therapy does not produce vitamin D and cannot correct vitamin D deficiency. Only UVB light has the right amount of energy to kick off the chemical reaction in your skin that makes vitamin D.
Is red light therapy the same as UV light therapy for vitamin D production?
Not at all. UVB therapy is what triggers vitamin D synthesis. Red light therapy uses completely different wavelengths and supports completely different biological processes.
What are the benefits of red light therapy compared to UV light therapy?
Red light therapy focuses on cellular repair, inflammation support, recovery and skin health all without UV exposure. UVB light therapy helps the body make vitamin D but comes with risks like tanning, burning and long-term skin damage if misused.
Is red light therapy safe for all skin types?
Yes. Because red light therapy does not utilise ultraviolet wavelengths. It doesn’t burn, tan or damage the skin. People with all skin tones and sensitivities generally tolerate it well.
Can red light therapy be combined with vitamin D supplementation?
Absolutely. They don’t interfere with each other. Just remember: supplements and UVB exposure can raise vitamin D levels red light therapy can not.
Sources:
1. Bikle, D. D. (2025, June 15). Vitamin D: Production, metabolism, and mechanism of action. In K. R.
Feingold, R. A. Adler, S. F. Ahmed, et al. (Eds.), Endotext. MDText.com, Inc.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278935/
2. Herrera, M. A., Ribas, A. P., et al. (2024). Red-light photons on skin cells and the mechanism of
photobiomodulation. Frontiers in Photonics, 5, 1460722. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphot.2024.1460722
3. Abe, Y., Konno, H., Yoshida, S., Yamauchi, T., Yamasaki, K., Denda, M., et al. (2019). Red
light–promoted skin barrier recovery: Spatiotemporal evaluation by transepidermal potential. PLOS
ONE, 14(7), e0219198. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219198
4. Naeem, Z. (2010). Vitamin D deficiency—An ignored epidemic. International Journal of Health
Sciences (Qassim), 4(1), V–VI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068797/
5. Cui, A., Zhang, T., Xiao, P., Fan, Z., Wang, H., & Zhuang, Y. (2023). Global and regional prevalence of
vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 7.9 million
participants. Frontiers in Nutrition, 10, 1070808. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2023.1070808
6. Chandra P, Wolfenden LL, Ziegler TR, Tian J, Luo M, Stecenko AA, Chen TC, Holick MF, Tangpricha V.
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency with UV light in patients with malabsorption syndromes: a case series.
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2007 Oct;23(5):179-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-
0781.2007.00302.x. PMID: 17803596; PMCID: PMC2846322.
7. Heiskanen, V., Pfiffner, M., & Partonen, T. (2020). Sunlight and health: Shifting the focus from vitamin
D₃ to photobiomodulation by red and near-infrared light. Ageing Research Reviews, 61, 101089.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101089
8. NHS. (n.d.). Vitamin D. NHS. Retrieved January 11, 2026, from
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-d/
Does Red Light Therapy Help Vitamin D? | Trophyskin-health
How to Increase Vitamin D Levels with Red Light Therapy | Exercising Health
Red Light Therapy: Benefits, Side Effects & Uses | Cleveland Clinic
Can Red Light Therapy Improve Sleep, Skin, and Recovery? | News Medical
Vitamin D Deficiency- An Ignored Epidemic | PMC
Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment | Cleveland Clinic